Add tools
To handle queries that your chatbot can’t answer “from memory”, integrate a web search tool. The chatbot can use this tool to find relevant information and provide better responses.
The results are page summaries our chat bot can use to answer questions:
We can now incorporate it into a
6. Define the
With the tool node added, now you can define the
 Congratulations! You’ve created a conversational agent in LangGraph that can use a search engine to retrieve updated information when needed. Now it can handle a wider range of user queries. To inspect all the steps your agent just took, check out this LangSmith trace.
Congratulations! You’ve created a conversational agent in LangGraph that can use a search engine to retrieve updated information when needed. Now it can handle a wider range of user queries. To inspect all the steps your agent just took, check out this LangSmith trace.
This tutorial builds on Build a Basic Chatbot.
Prerequisites
Before you start this tutorial, ensure you have the following:- An API key for the Tavily Search Engine.
1. Install the search engine
Install the requirements to use the Tavily Search Engine:2. Configure your environment
Configure your environment with your search engine API key:3. Define the tool
Define the web search tool:4. Define the graph
For theStateGraph you created in the first tutorial, add bind_tools on the LLM. This lets the LLM know the correct JSON format to use if it wants to use the search engine.
Let’s first select our LLM:
StateGraph:
5. Create a function to run the tools
Now, create a function to run the tools if they are called. Do this by adding the tools to a new node calledBasicToolNode that checks the most recent message in the state and calls tools if the message contains tool_calls. It relies on the LLM’s tool_calling support, which is available in Anthropic, OpenAI, Google Gemini, and a number of other LLM providers.
If you do not want to build this yourself in the future, you can use LangGraph’s prebuilt ToolNode.
6. Define the conditional_edges
With the tool node added, now you can define the conditional_edges.
Edges route the control flow from one node to the next. Conditional edges start from a single node and usually contain “if” statements to route to different nodes depending on the current graph state. These functions receive the current graph state and return a string or list of strings indicating which node(s) to call next.
Next, define a router function called route_tools that checks for tool_calls in the chatbot’s output. Provide this function to the graph by calling add_conditional_edges, which tells the graph that whenever the chatbot node completes to check this function to see where to go next.
The condition will route to tools if tool calls are present and END if not. Because the condition can return END, you do not need to explicitly set a finish_point this time.
You can replace this with the prebuilt tools_condition to be more concise.
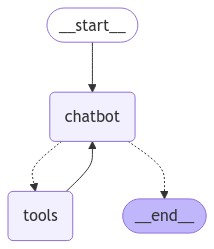
7. Visualize the graph
You can visualize the graph using theget_graph method and one of the “draw” methods, like draw_ascii or draw_png. The draw methods each require additional dependencies.

8. Ask the bot questions
Now you can ask the chatbot questions outside its training data:9. Use prebuilts
For ease of use, adjust your code to replace the following with LangGraph prebuilt components. These have built in functionality like parallel API execution.BasicToolNodeis replaced with the prebuilt ToolNoderoute_toolsis replaced with the prebuilt tools_condition

